Voting System Complete Capstone Documentation
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
The election process allows the general population to choose their representatives and express their preferences for how they will be governed. Naturally, the integrity of the election process is fundamental to the integrity of democracy itself. The election system must be sufficiently robust to withstand a variety of deceptive behaviors and must be sufficiently transparent and comprehensible that voters and candidates can accept the results of an election. Election fraud and delayed process of electoral selection were common problems in any kind of voting system.
Voting is a method for a group such as a meeting or an electorate to make a decision or express an opinion—often following discussions, debates, or election campaigns. It is often found in democracies and republics. Electronic voting (also known as e-voting) is a term encompassing several different types of voting, embracing both electronic means of casting a vote and electronic means of counting votes. Electronic voting is often seen as a tool for making the electoral process more efficient and for increasing trust in its management. Properly implemented, e-voting solutions can increase the security of the ballot, speed up the processing of results and make voting easier. However, the challenges are considerable. If not carefully planned and designed, e-voting can undermine the confidence in the whole electoral process.
For many years, Paper-based Voting Systems (PVS) a paper-based ballot is used as a way to vote during campus election day. The process involves the following: record, count, and produce a tabulation of the vote count from votes that are cast on paper cards or sheets. This matter put an inefficient way of voting process as students have to queue up to register their name before they can vote. Furthermore, the traditional way of voting will take a long process and is time consuming.
With the advent of modern technology, the automated voting processes through the use of information technology would be a straightforward application that would improve efficiency and would avoid problems that plagued the election. A number of effects on the automated voting system have been carried out worldwide. These are: increased participation of student voters, greater voter convenience in terms of voting time, produced accurate and reliable results.
The election process is using the traditional way of voting. A paper-based ballot is used as a way to vote during Election Day. For this reason, the researchers have decided to design and develop automated voting software that is user-friendly and reliable.
In this study, the researchers aims is to develop a computer based voting system that is accurate, reliable, and easy to use during the election of student representatives and to provide relevant and accurate information needed after the election process.
Project Context
Our subject respondent is using the traditional way of voting in their election process where students will have to line up and register their name before they can vote. The students will collect their ballot, write their chosen candidate, submit their ballot, and have their fingernails inked. The counting of process is another problem. After the given election period, the members of the electoral board will have to count the votes manually which is a very tedious task and is prone to errors. Thus, manual counting may result to inaccurate and unreliable results.
In this study, the researchers aim to develop an efficient, accurate and reliable computer-based voting system for the students that could track ballots, speed the counting of ballots and can facilitate electoral fraud. The design of electronic voting system will be based upon the electoral process adopted by the school. The system can be made fully accessible to any computers; information of the student candidates such as their pictures and accomplishments in which the student can identify and determine easily their respective candidate.
The software includes important features such as user’s log access, voter’s page, admin page, database maintenance, and help assistant.
Thus, this project will focus on how to design and develop a computer based voting system adopting the direct recording electronic voting to be used by the school during election period.
Purpose and Description
The main purpose of this capstone project is to develop automated voting software that is user-friendly and reliable. The Electronic Voting System (VOTING SYSTEM) will be developed by the researchers for high school and college level. The proposed project “Electronic Voting System is a computer based software that enables voters to vote smoothly, comfortably, and peacefully during student government elections The VOTING SYSTEM enables users to interactively view profiles of the candidates and choose their candidates in an electronic screen, through buttons, a mouse-based GUI or by simply using an input device to make their choices. The system will focus on the school’s election which will allow voters to vote using a computer and the system will provide accurate voting results.
The features of the system will focus on: log-in/log-out services, administrator’s page, voter’s page, database maintenance, and help assistant. Log-in/Log-out Services, refers to one of the features of the proposed system that will prompt users to enter their user ID and password to be able to access the student voter’s page and the school administrator’s page. Voter’s Page, is used by the student voters to view candidates party list and candidates profile, and cast their votes during election period. Administrator’s Page, is used to register and validate new voters, existing voters, candidates’ record, and generate election voting results. Database Maintenance, refers to one of the features of the system wherein the administrator can update voters’ records, candidates’ record, manage data and transaction log files, and backup the system. Help Assistant, which contains instructions on how to use the system.
The proposed project can generate the following outputs, these are: user’s log report, candidate party list, and election tabulation results.
The proposed project offers several benefits for the school administration and the student voters which include the following: voters can easily cast their votes, voters can choose their candidates through an electronic screen or computer monitor by a click of a mouse, speeds up the counting of votes, increase the security and reliability of elections, computer can count an unlimited number of ballots, and the system can automatically generate the results to determine the winning candidates.
Objective of the Study
The main objective of this project is to develop a computer based voting system, Electronic Voting System (VOTING SYSTEM) for high school and college level, that is accurate, reliable, and easy to use during the election of student representatives and to provide relevant and accurate information needed after the election process.
Specifically, this project aims to:
- Provide voting software that is fully accessible through Local Area Network (LAN) of the school.
- Provide a direct recording voting system where voters view ballots on a computer monitor and makes choices using an input device.
- Provide results of the election that is fast, reliable and accurate.
- Provide help guide feature to guide voters on how to use the system.
Scope and Limitations of the Study
The study will focus on the development of a computer based voting system for the students of high school and college level. The VOTING SYSTEM shall be installed in the main server and shall be limited to the students who are officially enrolled to access the system. The database maintenance will focus on adding, editing, and deleting candidates running for student government position and electoral board members, maintaining and managing table entries of users and user’s log; and monitoring of user’s activities in the system.
The proposed project will be implemented through the local Intranet connectivity of the school. This is not accessible through the World Wide Web and only the Office of the Dean of students is only authorized person who has the full access of the system after the election period.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE/SYSTEMS
This chapter presents the review of the related literature and studies that will enable the researchers to acquire basic information and references in the present study, and the technical background of which will discuss the technicality of the project, details of the technologies to be used and the relevance of the project.
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
Electronic Voting
According to Wikipedia.org (2012) Electronic voting (also known as e-voting) is a term encompassing several different types of voting, embracing both electronic means of casting a vote and electronic means of counting votes. It can include punched cards, optical scan voting systems and specialized voting kiosks (including self-contained direct-recording electronic voting systems, or DRE). It can also involve transmission of ballots and votes via telephones, private computer networks, or the Internet. Electronic voting technology can speed the counting of ballots and can facilitate electoral fraud.
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_voting)
Benefits of Electronic Voting System for Voters
According to www.vaalit.fi (2008) electronic voting presents numerous advantages over traditional paper ballot voting. The advantages of an electronic voting system can be divided into advantages for the voters and advantages for the authorities. Advantages of electronic voting for the voters includes: electronic voting speeds up the voting process and increase the security and reliability of elections where electronic vote is transported safely, reliably and fast into the centralized electronic ballot box. Further, in electronic voting it is not possible to make voting errors by mistake, because the identification information of the chosen candidate will appear on the screen before the vote is confirmed. Another advantage for the voter is that there is no ambiguity in interpreting an electronic vote. When traditional paper ballots are used, unclear numbers may sometimes cause problems.
(http://www.vaalit.fi/sahkoinenaanestaminen/en/etuja.html)
Benefits of Electronic Voting System for Authorities
According to www.vaalit.fi (2008) advantages of electronic voting for the authorities are as follows: electronic voting reduces and simplifies the work of the authorities significantly; electronic voting leads to notable cost savings through reduced personnel; reduce cost for example various forms and documents are no longer needed; electronic votes can be counted fast and reliably, and the result of the vote will be ready almost immediately.
(http://www.vaalit.fi/sahkoinenaanestaminen/en/etuja.h
Direct Recording Electronic voting
Haupt (2008) described a different voting process that could be considered “electronic voting”. According to Haupt there exists a paper based system that uses computers to count the actual ballots; however the original paper ballot is still intact. Direct Recording Electronic (DRE) voting is a voting machine that does not use a paper ballot like the paper based electronic voting machines. Instead, people choose their candidates and proposals through an electronic screen, either through buttons or through a more modern approach, touch screen. DRE voting machines also have the advantage of never running out of paper ballots at a polling center, since the computer can count an unlimited number of ballots.
(http://voices.yahoo.com/electronic-voting-good-bad-2085596.html)
The Voting Process
On February 25, UP Diliman(UPD) held its first campus-wide computerized University Student Council (USC) elections. The open source voting system, called “Halalan”, was created by the UP Linux Users Group (UnPLUG), a student organization at the College of Engineering (CoE). The colleges provided the computers for the elections. The voting process started with students presenting their IDs or Form-5s to attending poll clerks, who checked the list of valid voters. Students on the list then received their passwords from the poll clerks and proceeded to unoccupied voting stations. Using their student numbers and the passwords provided as login information, they opened their electronic ballots and marked the boxes of their chosen candidates. Once they clicked the confirm button, their votes were final and they were automatically logged out. The system allows voters to log in again but only to check their votes, not change them. The first working prototype of Halalan was created in January 2005 and presented to UPD student councils and student publications later that month at the Palma Hall Lobby. Its first application in the USC elections was at the CoE and the School of Statistics in 2007. A year later, the College of Business Administration, the College of Mass Communication, and the School of Library and Information Science also adopted the system.
(http://iskwiki.upd.edu.ph/index.php)
Synthesis
The concept and ideas that the researchers have gathered came from various authors and professionals are related to the study which the researchers used to support the study. The literatures and studies gathered and presented in this chapter gave the researcher insights, facts, and adequate information that will serve as the basis, guide, and reference that are relevant and necessary in the development of VOTING SYSTEM.
The background and importance of electronic voting technology serve as foundation in the development of a VOTING SYSTEM. The lists benefits or advantages of electronic voting system to the voters and administrators are relevant the researchers in the conduct of the present capstone project because these serve as bases in the major concerns of the study, particularly in the features that should be included in the development of the VOTING SYSTEM, and also in the implementation of the system. While the related studies/systems serve as basis of the researchers about the systems that were developed that has relation to the proposed project.
TECHNICAL BACKGROUND
The existing voting system is purely manual using paper ballot. The paper ballot is still used in many areas of the country specially colleges and universities for their selection of student leaders. The school does not currently utilize its existing technology that is necessary to speed up the voting process and the tabulation of results.
The current technology is adequate enough for implementation of the proposed system. Although it has computer units, local area network connectivity, internet connection, and machine for printing results, the school does not have software or a computer-based voting system.
The use of an electronic voting system and taking advantage of the new technology will make their student services better.
The proposed VOTING SYSTEM shall be installed on a main server and will have a back-up server which is intended to provide a secondary storage for data in case of breakdown of the main server. The Microsoft Server 2003 Enterprise Edition will be used as operating system for the servers running applications such as networking and databases. A software firewall shall be configured in the main server to protect the server and other computers in the network from backdoor applications, Operating system bugs, and Viruses.
The back-end user of the proposed system is the Dean of Students who will stand as the administrator of the computer-based voting system. The admin must register the students in order to access the voting system during election period. The front-end users are the students who will be voting for their candidate.
The proposed VOTING SYSTEM software will utilize the Modified Waterfall Model in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like waterfall) through the phases of Conception, Initiation Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production, implementation and Maintenance.
CHAPTER 3
METHODOLOGY
This chapter deals with the method used by the researchers in conducting the study, the system development method used, and its results and discussion.
The researchers will utilize several analytical tools to help and justify the conduct of the study and also guide the researchers to resolve the problems encountered by the school administrators and student voters in the election process. The analytical tools include interview, observation and brainstorming which will be employed by the researchers in analyzing the problems of the existing system.
Interviews are a common technique used to determine the user’s wants, needs and requirements. An interview is a conversation between two people (the interviewer and the interviewee) where questions are asked by the interviewer to obtain information from the interviewee. The researchers will prepare an interview guide composed of list of questions to help researchers in the interview.
Observing is the study of the expected users. By observing users, an analyst can identify a process flow, awkward steps, pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Brainstorming is used in requirements elicitation to get as many ideas as possible from a group of people. Generally used to identify possible solutions to problems, and clarify details of opportunities. Brainstorming casts a wide net, identifying many different possibilities. Prioritization of those possibilities is important to finding the solutions to the problem of the existing system.
On system development, the researchers will utilize the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) method in the development of the system. The SDLC method is the process employed in the analysis and design of the VOTING SYSTEM as shown in Figure 1.
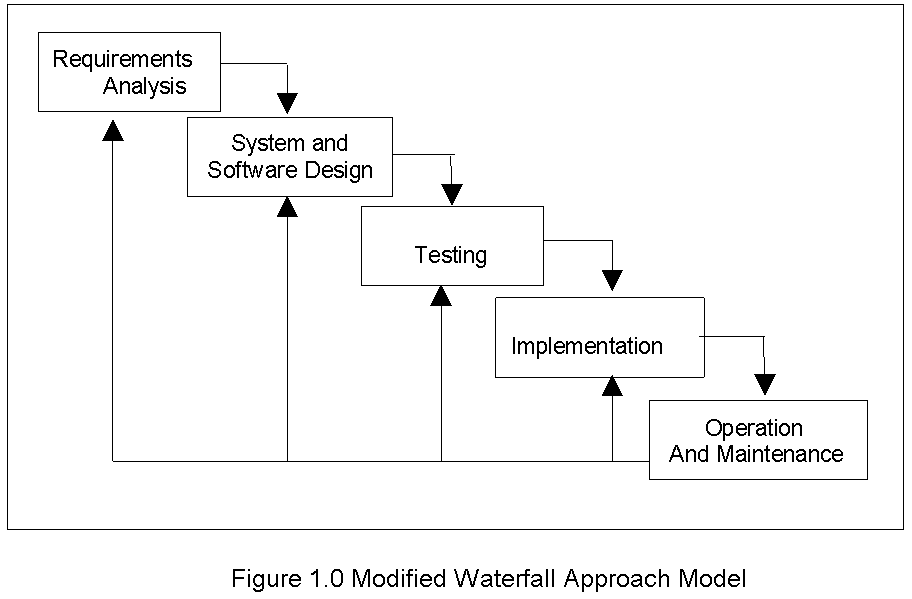
Figure 1.0 Modified Waterfall Approach Model
Figure 1 illustrates the Modified Waterfall Model that will be used by the researchers in developing the Electronic Voting System. The model develops systematically from one phase to other in a downward fashion, like a waterfall. It is made up of several phases and the details of these phases are:
Requirement Analysis. In this phase, the researchers will study how the system works, determine the user’s wants, needs and requirements, and recommend a solution. It also involves developing estimates for the work to be performed, establishing the necessary commitments, and defining the plan to perform the work.
System and Software Design. On this phase, the system will be designed based on the requirements needed in the system. Process modelling and data modelling will be done to present the system’s data and the relationship between different data elements. Data Flow Diagram (DFD) will be used to represent the flow of data in the system. Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) shall be employed as data model for the system. After finalizing the ERD, the system database will be created to fulfil the system’s information and processing needs. The programmer will create the source codes necessary for the system to be constructed.
Testing. This phase aimed to find out whether the software functions and features work according to the specification, ensure that the produced system is complete and performs efficiently, evaluate whether the software perform all activities after integration with the existing operating environment, and measure up the reliability and overall quality of the software.
Implementation. In this phase, the researchers will conduct the system dry-run and conduct training of the target users of the system. The users of the system will check if the recommended functions and suggestions of the users are met.
Operation and Maintenance. This Phase is to ensure the information system is fully functional and performs optimally until the system reaches its end of life. The Operations and Maintenance Phase comprises the following: management of changes to the system to support end users, monitoring of system performance, performance of required security activities such as backups, and continuation of end user support through training and documentation
Requirements Analysis and Documentation
The proposed system is “Electronic Voting System”, an application that enables users to vote using a computer. The VOTING SYSTEM application will enable users to interactively choose their candidate and cast their vote using a mouse-based GUI.
The completion of the software depends upon meeting the following goals and objectives:
- Provide voting software that is fully accessible through Local Area Network (LAN) of the school.
- Provide a direct recording voting system where voters view ballots on a computer monitor and makes choices using an input device.
- Provide results of the election that is fast, reliable and accurate.
- Provide help guide feature to guide voters on how to use the system.
System Functionality
VOTING SYSTEM Administrator – One of the features of VOTING SYSTEM is the log-in and log-out services which require users to enter user id and password. It has a database that can be updated and maintained by the admin. The administrator is the only authorized user of the system who can generate results and tally of votes from the system.
VOTING SYSTEM Voter – The student voters are prompt by the system to enter their user id and password. Voters can choose their candidate and cast their votes automatically by a click of a button.
Project Plan
Before the software project is implemented, the researchers will prepare a project schedule that identifies the anticipated activities involved, management of resources and project plans showing the cost needed in the development of the voting system.
Design of Software and Process
Based on the result of the observation and interview as well as users suggestions the researchers created a design for the system to be developed. All the requirements of the first phase are being used to contribute in the successful preparation of creating the Electronic Voting System for high school and college students. It also includes the Data Flow Diagram, DFD Explosion for teachers and students, and Entity Relationship Diagram of the developed system.
Development and Testing
The researchers will use the Modified Waterfall Model in developing the VOTING SYSTEM. In this methodology, the software evolved as a result of shared information between the respondents and the researchers.
Testing will exercise the system in all possible ways. It includes initial testing and final testing of the new software. The electronic voting systems, including equipment and software, should be tested prior to the deployment of to help ensure that the system works as expected.
Requirements Definition Phase
During the Requirements Definition Phase, the researchers together with the beneficiary of the proposed system will work together to establish the architectural boundaries for the project, to establish criteria for measuring the technical performance of the system, and to baseline the requirements. Activities in this phase are the following: define system requirements, develop system process model, and develop application logical data model, estimate system workload, and Identify strategies for training end users.
Software Requirements. The software development tools for this study are presented in Table 1.0.
Software Requirements
Visual Basic – Visual Basic is a third-generation event-driven programming language from Microsoft for its Component Object Model (COM) programming model first released in 1991 and declared legacy during 2008. Microsoft intended Visual Basic to be relatively easy to learn and use. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visual_Basic)
Microsoft Access – Microsoft Access is a Database Management System (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Microsoft Jet Database Engine with a graphical user interface and softwaredevelopment tools. It is a member of the Microsoft Office suite of applications, included in the professional and higher editions. (https://www.tutorialspoint.com/ms_access/ms_access_overview.htm)
Hardware Requirements. The researchers presents the minimum hardware resources necessary for the VOTING SYSTEM and is presented in Table 2.0
Table 2.0 Hardware Requirements
Hardware requirements
- Intel Dual Core or Higher Processor
- 512 MB to 1 GB Memory (Recommended)
- 80 GB, Hard Disk
- Dual Lan Card
- Standard Keyboard
- Standard Mouse
- AVR/UPS
- Switch
- Monitor
- Printer
Peopleware Recommendation. Table 3.0 includes the recommendation of appropriate users for the new system with specific task given.
The system is intended for beginners and professional users. Its design and uses suit the needs of the student voters as well as to the administrator to provide an accurate and effective voting and tabulating machine in the election process and that provides the user accurate results.
Table 3.0 Peopleware Recommendation
Software Developers:
Project Manager – Supervises and monitors the entire project activities and its development.
System Analyst – Responsible for researching, planning and recommending software and system choices to meet an organization’s business requirements.
Programmer – Creates the source codes for the development of proposed system. Must be expert with the programming language to be used in the development of the system.
Researchers – Further researchers on the content and other studies related to current system being developed.
Recommended Users:
Back-end user:
VOTING SYSTEM Administrator – In charge of maintaining and managing the table entries of files; keeps the server up, running, and secure; keeps track of the log; updates the database, provides access to authorized users of the system.
Front-end users:
Students/Voters – One who have access to the computer-based voting system.
System Process Model. The researchers present the context diagram and the decomposition diagrams of the proposed voting system which show the procedures of each function, the users and the expected outputs.
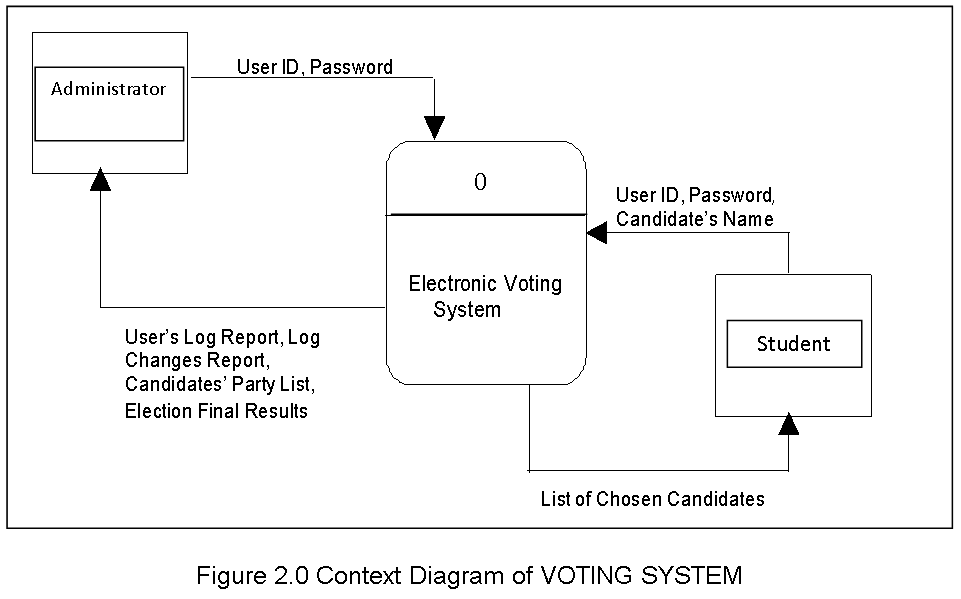
Figure 2.0 Context Diagram of VOTING SYSTEM
The context diagram of VOTING SYSTEM in Figure 2.0 illustrates the users input to the system and the output information to the users. System Administrator and the student voters are the users of the system. The system can provide the following to the users: user’s log report, log changes report, candidates’ party list, election final results, and list of candidates chosen by the voter.
Implementation and Unit Testing Phase
This section will discuss the implementation plan and unit testing of the proposed system. This phase will also discuss if the recommended functions and suggestions of the respondents and users are met.
The construction of the project is divided in modules/units and is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated in the next phase. Testing is one of the important phases of the VOTING SYSTEM development. Testing will exercise the system in all possible ways to test it for potential errors and bugs. It includes initial testing and final testing of the proposed electronic voting system. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality; this is referred to as Unit Testing. Unit testing mainly verifies if the modules/units meet their specifications.
Integration and System Testing Phase
Integration and system testing is a type of software testing, this makes sure that tests such as the new system and integration are done before releasing the software. Software testing has very strict set of rules and guidelines that it follows to make sure each individual part of the software is thoroughly checked before it is given the OK, this makes sure that there are no errors and that the software runs how it’s supposed to. Integration and system testing will be done by the researchers and will focus on the software testing phase in the system development life cycle.
Integration testing in the software testing model comes before system testing and after the unit testing has been done.
System testing is simply testing the new software as a whole; it gets all the integrated modules of the various components from the integration testing phase and combines all the different parts into a system which is then tested. Testing is then done on the system as all the parts are now integrated into one system the testing phase will now have to be done on the system to check and remove any errors or bugs.
Operation and Maintenance Phase
System operation includes user support to the end user or users which is an integral part of the election process operations. The Dean of students (VOTING SYSTEM administrator) and the students (VOTING SYSTEM voters) are the users of the proposed voting system. Users should receive training especially the VOTING SYSTEM administrator. The EV admin could use the user’s manual or the help guide integrated into the newly developed system.
The maintenance-phase consists of maintenance-tasks to keep the product up and running. The researchers will continuously monitor the performance of the system in regard to hardware and the network. Daily operations of the system require identifying and implementing minor modifications for it to function optimally and correctly. The researchers will document these modifications. This phase includes any general enhancements, changes and additions, which might be required by the end-users. The defects and deficiencies are usually documented by the developing organization to enable future solutions and known issues addressing in any future maintenance releases. Maintenance is always necessary to keep system usable and useful.
System Prototype
This section will present the needed report layouts and screen forms of the developed system. The researchers will provide hard copy documents for the new system such as candidates’ party list and actual election voting results. The researchers will present the screenshot layouts of VOTING SYSTEM to give readers an overview on what the system looks like.
Implementation Plan and Result
After the initial testing and final testing, the researchers plan to integrate the Electronic Voting System to its target users during campus election day and to check if the recommended functions and suggestions of the users are met.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
En.wikipedia.org (2012). Electronic Voting. Retrieved October 15, 2012 7:00 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_voting.
Haupt, Thomas (2008). Electronic Voting: What is Good and What is Bad. Retrieved October 20, 2012 6:00pm from http://voices.yahoo.com/
electronic-voting-good-bad-2085596.html
Kumar, D. Ashok and T. Ummal Sariba Begum (2011). A Novel design of Electronic Voting System Using Fingerprint. International journal of innovative technology & creative engineering (issn:2045-8711) vol.1 no.1 January 2011. Retrieved from http://ijitce.co.uk.
Sehlhorst, Scott (2006). Ten Requirements Gathering Techniques. Retrieved October 12, 2012 8:00pm from http://tynerblain.com/blog/2006/11/21/
ten-requirements-gathering-techniques/
www. vaalit.fi (2008). Advantages of electronic voting for the voters. Retrieved October 20, 2012 6:00pm from http://www.vaalit.fi/
sahkoinenaanestaminen/en/etuja.html