Daily Time Record System Database Design
The capstone project entitled “Daily Time Record System” is a multi-company platform that will allow them to monitor the time-in and time-out of their employees.
This article will provide you with the list of tables and field/columns for every table in the design of database structure/schema of daily time record system. The team will later provide a video tutorial on how to create the database in PHPMyAdmin.
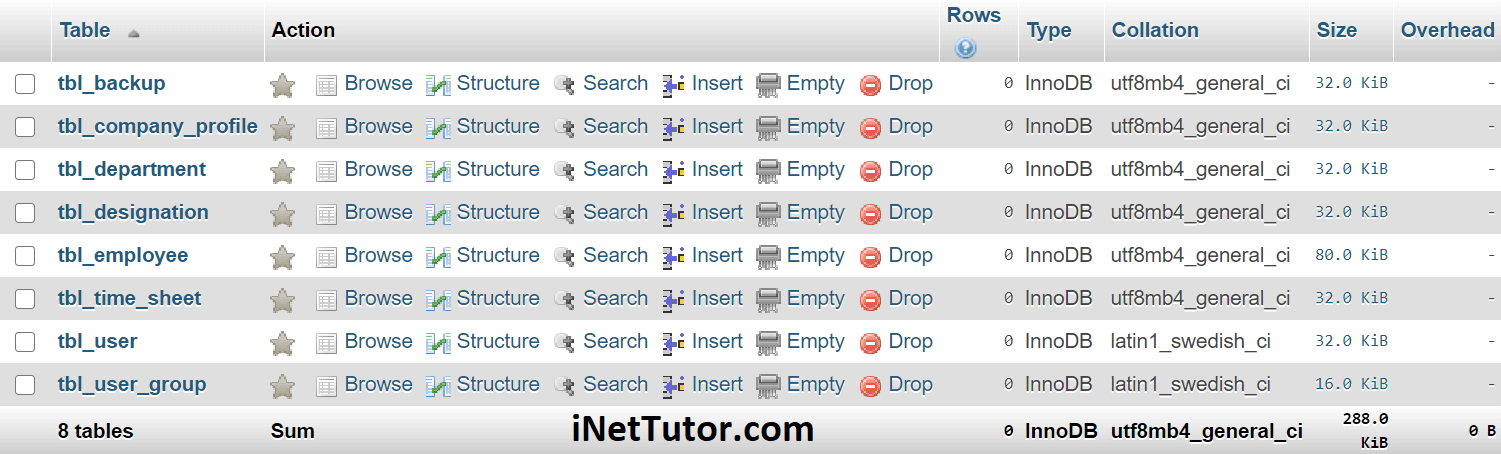
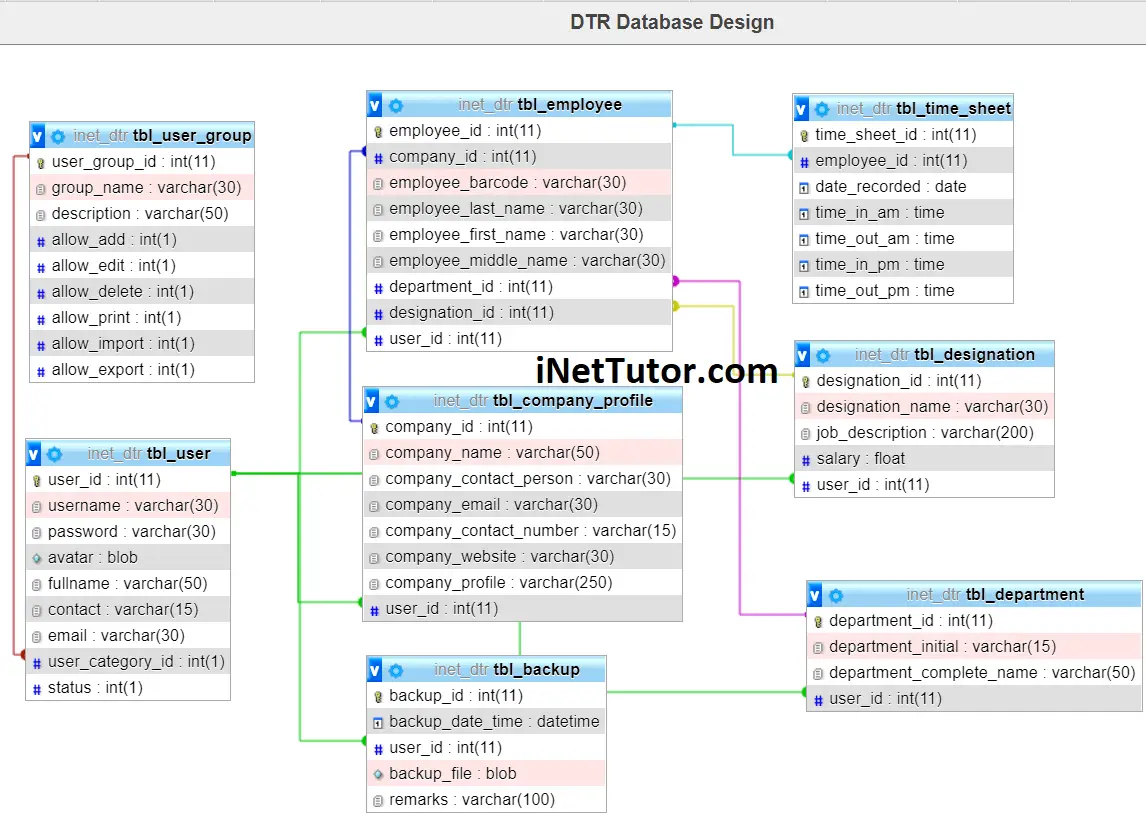
This database design has 8 tables with their respective fields and columns as well as their relationships among each other.
tbl_employee – this is the table that stores the information of the employees. The employee table has 9 columns.
- employee_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- company_id – this is a foreign key that links to the company profile of the employee.
- employee_barcode – a unique code combination given to the employee. In most cases this is also the employee number.
- employee_last_name – last name of the employee.
- employee_first_name – first name of the employee.
- employee_middle_name – middle name of the employee.
- department_id – this is a foreign key that links to the department table. This is where the employee is assigned.
- designation_id – this is a foreign key that links to the designation table. This is position of the employee in their organization.
- user_id – the user who accepts/approve/deactivate the employee profile. It is a foreign key that connects to the user table.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_employee, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_employee` ( `employee_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `company_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `employee_barcode` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `employee_last_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `employee_first_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `employee_middle_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `department_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `designation_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_department – department table stores the information of the different departments or sections of the organization or company. The table has 4 columns.
- department_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- department_initial – initial name of the department.
- department_complete_name – complete name of the department.
- user_id – the user who accepts/approve/deactivate the department profile. It is a foreign key that connects to the user table.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_department, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_department` ( `department_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `department_initial` varchar(15) NOT NULL, `department_complete_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_designation – the employee position or assignment is stored in this table. Designation table has 5 columns.
- designation_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- designation_name – name of the position, assignment or designation.
- job_description – specific job roles of a certain job position.
- salary – basic salary of the job position.
- user_id – the user who accepts/approve/deactivate the department profile. It is a foreign key that connects to the user table.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_designation, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_designation` ( `designation_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `designation_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `job_description` varchar(200) NOT NULL, `salary` float NOT NULL, `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_time_sheet – this table will store the time in and time our record of every employee. The time sheet table has 7 columns.
- time_sheet_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- employee_id – this column refers to the employee information, this is actually a foreign key that links to the employee table.
- date_recorded – date of attendance record.
- time_in_am – time in record of the employee in the morning.
- time_out_am – time out record of the employee in the morning.
- time_in_pm – time in record of the employee in the afternoon.
- time_out_pm – time our record of the employee in the afternoon.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_time_sheet, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_time_sheet` ( `time_sheet_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `employee_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `date_recorded` date NOT NULL, `time_in_am` time NOT NULL, `time_out_am` time NOT NULL, `time_in_pm` time NOT NULL, `time_out_pm` time NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_backup – the entire database needs to be copied in an external storage for back-up purposes and this table stores that information.
- backup_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- backup_date_time – date and time of the back-up process.
- user_id – the user who performs the back-up process. It is a foreign key that connects to the user table.
- backup_file – the backup file.
- remarks – important note or information about the back-up process.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_backup, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_backup` ( `backup_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `backup_date_time` datetime NOT NULL, `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `backup_file` blob NOT NULL, `remarks` varchar(100) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_company_profile – this table will store the information of the company. The table has 8 columns.
- company_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- company_name – the complete name of the company.
- company_contact_person – contact person of the company
- company_email – official email address of the company
- company_contact_number – contact information of the company (landline, mobile, etc)
- company_website – official website of the company (if any)
- company_profile – this column is open for any content such as the history of the company, services offered, and any other information about the company or shop
- user_id – the user who accepts/approve/deactivate the company profile. It is a foreign key that connects to the user table.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_company_profile, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_company_profile` ( `company_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `company_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `company_contact_person` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `company_email` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `company_contact_number` varchar(15) NOT NULL, `company_website` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `company_profile` varchar(250) NOT NULL, `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
tbl_user – this table will store the information of personnel who can access the records of the system.
- user_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- username – username of the personnel used to login together with the password.
- password – password of the personnel used to login together with the username.
- avatar – this will hold the profile image of the user.
- fullname – the complete name of the personnel or user.
- contact – contact number of the personnel (mobile/cellphone number).
- email – email address of the personnel/user.
- user_category_id – the user group or category of the user.
- status – the value of this column is 0 or 1, 0 means deactivated or inactive, 1 is activated or active.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_user, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_user` ( `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `username` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `avatar` blob NOT NULL, `fullname` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `contact` varchar(15) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `user_category_id` int(1) NOT NULL, `status` int(1) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
tbl_usergroup – this table store the information of the user group which includes the functions they can and can’t access in the system.
- user_group_id – primary key of the table. It is set usually to auto_increment (the database will automatically give this column a value starting from 1).
- group_name – name of the category or user group.
- description – information on what the user group is all about.
- allow_add – this column is to allow or prevent user from adding a record.
- allow_edit – this column is to allow or prevent user from editing or updating a record.
- allow_delete – this column is to allow or prevent user from removing or deleting a record.
- allow_print – this column is to allow or prevent user from printing a report.
- allow_import – this column is to allow or prevent user from importing records to the system.
- allow_export – this column is to allow or prevent user from exporting records from the system.
Create SQL Statement – the statement below is used to create the tbl_usergroup, copy the sql statement and paste it in the sql manager/tab of your phpmyadmin.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_user_group` ( `user_group_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `group_name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `description` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `allow_add` int(1) NOT NULL, `allow_edit` int(1) NOT NULL, `allow_delete` int(1) NOT NULL, `allow_print` int(1) NOT NULL, `allow_import` int(1) NOT NULL, `allow_export` int(1) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Indexes for dumped tables
-- -- Indexes for table `tbl_backup` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_backup` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`backup_id`), ADD KEY `user_id` (`user_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_company_profile` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_company_profile` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`company_id`), ADD KEY `user_id` (`user_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_department` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_department` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`department_id`), ADD KEY `user_id` (`user_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_designation` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_designation` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`designation_id`), ADD KEY `user_id` (`user_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_employee` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_employee` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`), ADD KEY `company_id` (`company_id`), ADD KEY `department_id` (`department_id`), ADD KEY `designation_id` (`designation_id`), ADD KEY `user_id` (`user_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_time_sheet` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_time_sheet` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`time_sheet_id`), ADD KEY `employee_id` (`employee_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_user` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_user` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`), ADD KEY `user_category_id` (`user_category_id`); -- -- Indexes for table `tbl_user_group` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_user_group` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`user_group_id`); -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for dumped tables -- -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_backup` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_backup` MODIFY `backup_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_company_profile` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_company_profile` MODIFY `company_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_department` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_department` MODIFY `department_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_designation` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_designation` MODIFY `designation_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_employee` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_employee` MODIFY `employee_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_time_sheet` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_time_sheet` MODIFY `time_sheet_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_user` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_user` MODIFY `user_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT; -- -- AUTO_INCREMENT for table `tbl_user_group` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_user_group` MODIFY `user_group_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT;
Constraints for dumped tables
-- -- Constraints for table `tbl_backup` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_backup` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_backup_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_company_profile` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_company_profile` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_company_profile_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_department` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_department` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_department_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_designation` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_designation` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_designation_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_employee` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_employee` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_employee_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user` (`user_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE, ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_employee_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`company_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_company_profile` (`company_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE, ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_employee_ibfk_3` FOREIGN KEY (`designation_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_designation` (`designation_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE, ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_employee_ibfk_4` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_department` (`department_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_time_sheet` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_time_sheet` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_time_sheet_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`employee_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_employee` (`employee_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; -- -- Constraints for table `tbl_user` -- ALTER TABLE `tbl_user` ADD CONSTRAINT `tbl_user_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`user_category_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_user_group` (`user_group_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; COMMIT;
Our team can modify the project based on your specific business requirements.
You may visit our facebook page for more information, inquiries and comments.
Hire our team to do the project.


