- Version
- Download 35
- File Size 53.35 KB
- File Count 1
- Create Date April 25, 2016
- Last Updated April 25, 2016
If Else Statement in C#
If Else Statement in C#
This is one of the basic things you need to learn not just only in c# but in every programming language you are going to study.
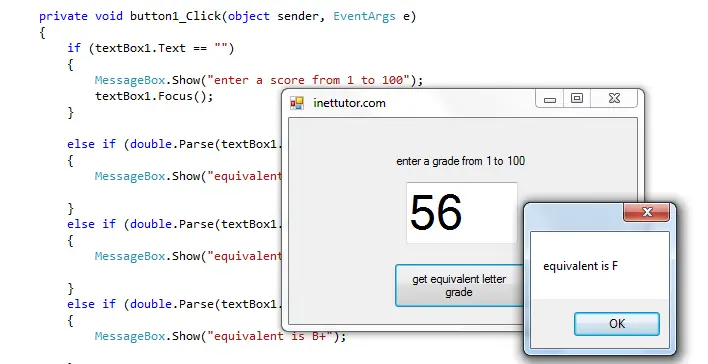
This is a sample program in c# that demonstrate how to use and functions of an if else statement.
Open the project solution (.sln) in visual studio 2010 or open directly the (.csproj)
Source code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "")
{
MessageBox.Show("enter a score from 1 to 100");
textBox1.Focus();
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) > 95 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 100)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is A");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) >= 90 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 94)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is A-");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) >= 87 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 89)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is B+");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) > 83 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 86)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is B");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) >= 80 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 83)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is B");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) >= 75 && double.Parse(textBox1.Text) <= 79)
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is C");
}
else if (double.Parse(textBox1.Text) < 75 )
{
MessageBox.Show("equivalent is F");
}
}
}
}